Abstract: This paper describes the structure and working principle of Komatsu engineering machinery electronic control diesel engine CRI fuel system, proposes the diagnostic process of common faults of CRI fuel system in Yunnan high-cold area, and analyzes it with maintenance service examples, in order to help Komatsu engineering machinery maintenance service personnel.
Introduction
At present, the common oil tank type electronic control fuel injection system used in diesel engines is more typical, including NEC’s ECU-U2 system, Catepillar’s HEUI system and BKM’s Servojet system. NEC’s ECU-U2 system does not have a flow damper on the common oil tank, making the structure of the injector more complicated. The diesel engine high-pressure control CRI (common oil tank direct injection) system jointly developed by Komatsu and Cummins of the United States completely separates the generation of injection pressure and the injection process from each other in a closed-loop system consisting of an injection pump, a pressure sensor, a flow damper and an ECU. The system can accurately control the fuel pressure in the common oil tank, meet the working needs of the diesel engine under different working conditions, greatly reduce the degree of change of the diesel engine fuel supply pressure with the engine speed, and enable the diesel engine to better meet the requirements of the power, economy and emission performance of engineering machinery.

According to statistics from Komatsu, 70% of engine failures are caused by poor management of oil, water and gas. Engineering machinery is often used in remote areas, and the working environment and fuel quality are not well guaranteed. In addition, the air in the high-altitude and cold areas of Yunnan is thin and the ambient temperature is low, which makes the Komatsu electronic diesel engine CRI fuel supply system frequently fail. This paper explains the structure and working principle of the CRI fuel system, combined with the analysis of common fault diagnosis and detection examples of Komatsu engineering machinery engine CRI fuel supply system in Lijiang, Yunnan Province, and proposes a logically clear fault diagnosis flow chart to facilitate maintenance service personnel to quickly and accurately diagnose and eliminate faults.
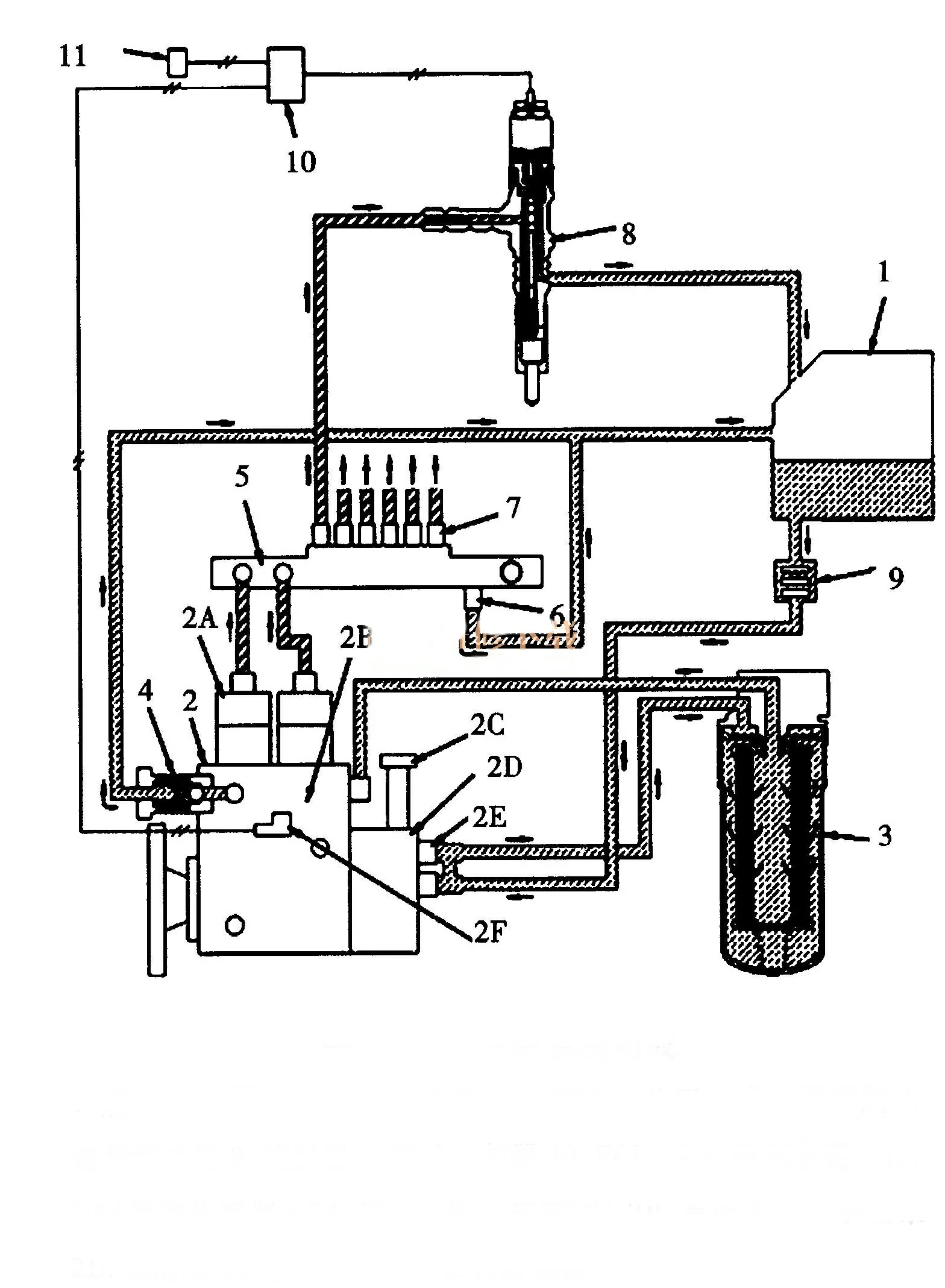
CRI fuel system structure and working principle
1. Fuel tank 2. Fuel supply pump 3. Fuel filter 4. Overflow valve 5. Common oil pipe 6. Pressure limiting valve 7. Flow buffer 8. Injector 9. Fuel cooler 10. ECU (engine controller) 11. NE (speed sensor) 2A. PVC (pressure control valve) 2B. High-pressure pump 2C. Manual pump 2D. Fuel supply pump 2E. Bypass valve 2F. G Rotation sensor
The CRI fuel system is mainly composed of injection pump, injector, common oil tank, ECU, and sensors such as speed and crankshaft angle position. The injection pump sends high-pressure fuel to the common oil tank, and the high-pressure fuel enters the injector of each cylinder through the common oil tank. The oil pressure in the common oil tank is detected by the pressure sensor and transmitted to the ECU. The system oil pressure is generally controlled at 120~130mPa.
CRI fuel supply system fault code and fault cause
Komatsu construction machinery comes with a monitoring panel that can display fault codes and alarms, which is convenient for on-site processing by service personnel. The monitoring panel is a set of fault detection self-diagnosis and display system based on OBD-II. When performing maintenance services, it is necessary to switch from operator mode to service mode. Table 1 shows the common fault codes and causes of the fuel supply system of Komatsu construction machinery engines. When there are alarms and fault code prompts, service personnel can perform corresponding fault detection and maintenance according to the prompts.
Analysis of common fault diagnosis and detection examples of CRI fuel supply system
When Komatsu construction machinery fails, the monitoring panel generally has clear fault codes and alarm prompts. However, there are also cases where failures occur without any prompts. Therefore, when performing fault diagnosis, on the one hand, it is necessary to detect according to the fault code prompts, and on the other hand, it is necessary to detect and diagnose according to the fault diagnosis flowchart formed based on experience. In the high-cold areas of Yunnan, the following two types of faults occur more frequently in the CRI fuel supply system faults of Komatsu construction machinery.
Fault diagnosis example analysis of abnormal fuel tank high pressure
In February 2010, a Komatsu PC240-8 excavator had a monitor alarm at the construction site of the Ningbo to Hugu Lake secondary highway in Ningbo County, Lijiang City. The display fault code is E979, and the fuel high pressure is abnormal. After checking, the diesel model is in accordance with the requirements. Loosen the fuel pump overflow valve joint, hit the hand oil pump, and oil overflows. Loosen the fuel tank overflow valve joint, start the engine, and oil overflows. It is suspected that the overflow pipe is blocked. Remove the diesel filter element and shake it. The diesel flowing out has a lot of impurities, so it is determined that the overflow pipe is blocked. After cleaning, assemble and return to the car, and the fault is eliminated.
Fault diagnosis example analysis of abnormal fuel pump no-load fuel supply
In March 2010, a Komatsu PC240LC-8 excavator at Lijiang Hugu Lake Airport had an alarm for abnormal fuel pump no-load fuel supply. The fuel meets the ambient temperature, but the oil quality is not good. It is suspected that the filter element may be blocked. There is no sign of oil leakage when the engine is stopped and at low total speed, and the diesel filter element is found to be blocked. It is judged that the diesel used in the machine has quality problems, which leads to the blockage of the filter screen of the diesel filter element, causing abnormal fuel pump no-load fuel supply. Replace the coarse filter element, start the engine, and the fault disappears. In December 2013, at a construction site of a Class 2 highway in Ningbo County, Lijiang City, a Komatsu WA500-6 loader equipped with a SAA6D140E-5 diesel engine was found. The diesel engine ran normally after starting, but the speed dropped from 1900 r/min to 800 r/min as soon as it was engaged in forward or reverse gear. There was no alarm on the display. Preliminary analysis showed that the oil pressure in the common rail tank was low. According to Figure 3, the low-pressure oil circuit was measured to be 0.19MPa, and the leakage of the pressure limiter was less than 10mL/min, both of which were normal values. The PVC valve was removed, the engine was shut down, and there was no fault code prompt in the electrical circuit. The above tests determined that the fuel injection pump was faulty. After replacing the fuel injection pump assembly, the fault disappeared.


